Loops benefit computer science students by saving their time while coding. It also helps them to reuse codes instead of writing codes all over from scratch. In this post I will teach you how to use Loops. As you follow along with the post, try to practice the activity along. Remember as a computer science student you learn more from practice.
LOOPS
Loops are a fundamental aspect of programming, and are used repeatedly to execute a block of code for a specified number of times, or until a certain condition is met. They are a key tool for automating repetitive tasks and are used extensively in a wide variety of applications.
There are several types of loops commonly used in programming, including:
- For Loops
- While Loops
- Do-While Loops
For Loops
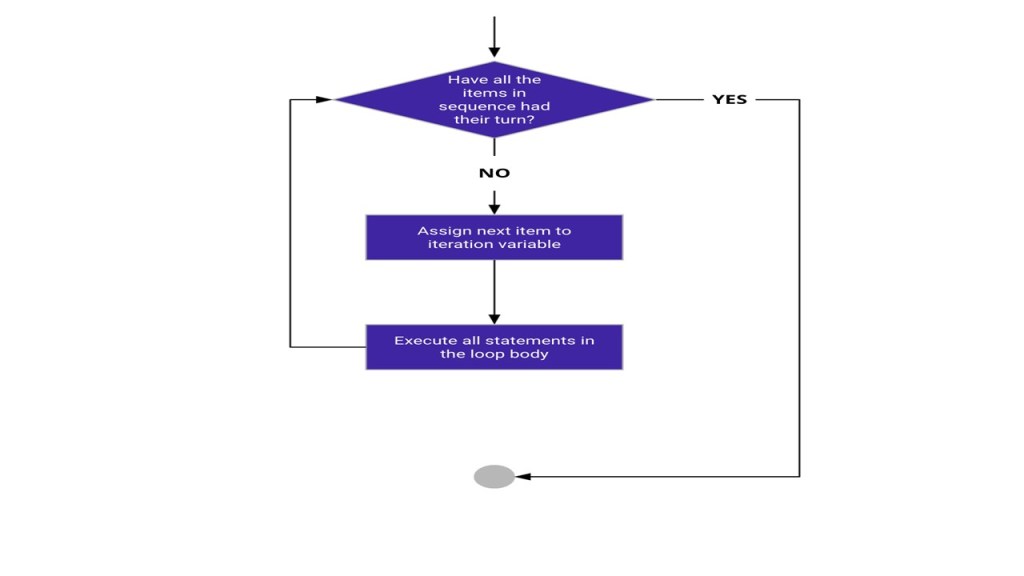
For loops are used to repeat a block of code a specified number of times. It is a good fit when we want to run a block of code a definite number of times, or when we want to iterate over a list of things. For loops are useful when you need to repeat a task a known number of times. See this example and you can copy the code to practice it.
for i in [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] : print(i)print(‘Blastoff!’)
The output will be:5
4
3
2
1
Blastoff!
While Loops
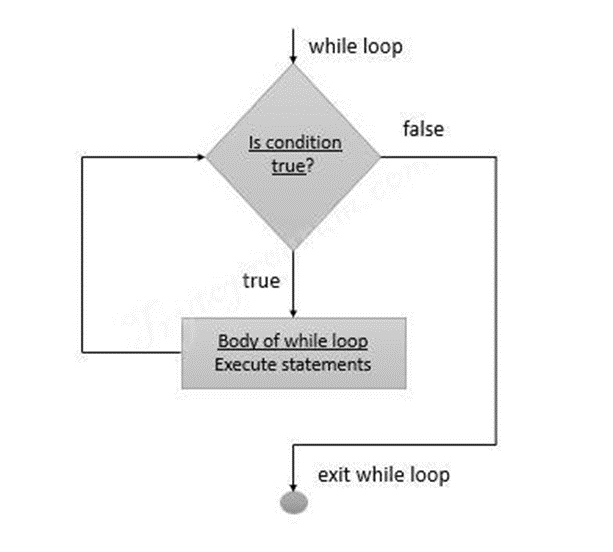
While loops are used to repeat a block of code as long as a specified condition is true. The condition is checked before each iteration, and the loop continues to execute as long as the condition remains true. While loops are useful when you need to repeat a task an unknown number of times. For example, we want a code to keep going like in the case of a password the program might ask a user for their password until they enter a valid password. The program doesn’t know ahead of time the number of tries the user will need. Instead, it knows when to stop asking. This type of situation is perfect for a while loop. There is a practical example below:
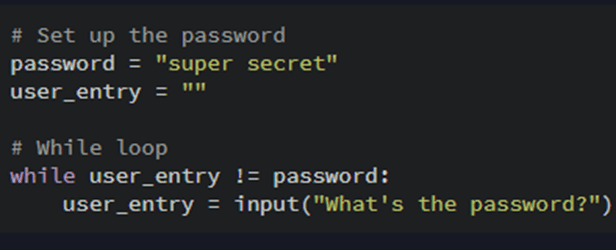
If you copied this example. You will notice the code keeps on running until you get the correct password.
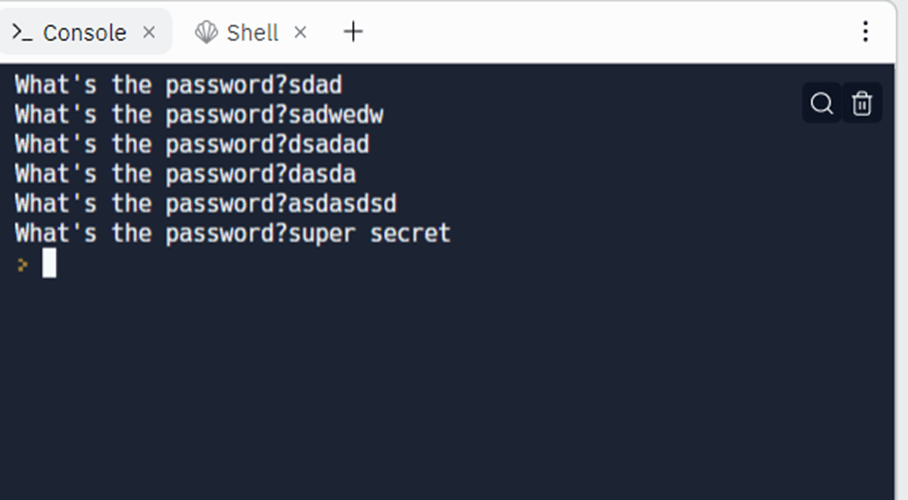
Try it out!
Do-While Loops
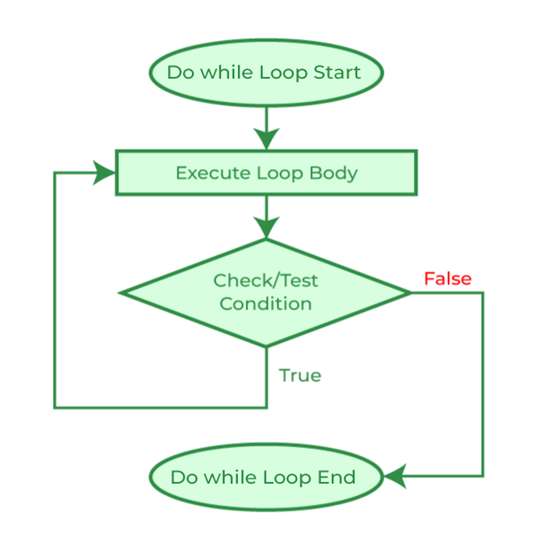
Do-while loops are similar to while loops, but the condition is checked after each iteration, rather than before. This means that the loop will always execute at least once. Another explanation is when the statements inside the loop body will be executed at least once even if the condition is never true. The do while loop is an exit-controlled loop, where even if the test condition is false, the loop body will be executed at least once. They are useful when you need to repeat a task an unknown number of times, but you know that the loop should execute at least once. Let us consider the example below:
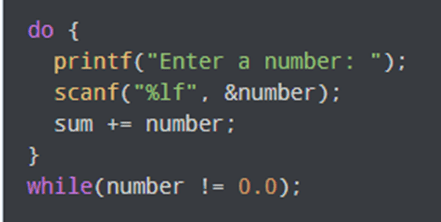
This prints out the program even if (number != 0.0)
Differences between For Loops, While Loops and Do While Loops
For loop:
- It is used when the number of iterations is known.
- In case of no condition, the loop is repeated infinite times.
- Initialization is not repeated.
- Statement of Iteration is written after running.
- Initialization can be in or out of the loop.
- The nature of the increment is simple.
- Used when initialization is simple.
While loop:
- It is used when the number of iterations is not known.
- In case of no condition, an error will be shown.
- Initialization is repeated if carried out during the stage of checking.
- It can be written at any place.
- Initialization is always out of the loop.
- The nature of the increment is complex.
- Used when initialization is complex.
Do While loop:
- The difference between While loop and Do While loop is that this loop checks for the body of a code before it runs the code.
- The difference between a For loop and a Do While is the same with that of While loop.
As a computer science student, it is important to note that loops can be nested, meaning that one loop can be inside another loop. This allows the program to be able to repeat an argument when a user enters an incorrect input., and is a powerful tool for solving a complex problem. Like you are given a project to create a password validator, using a loop can help with this.
Loops are a fundamental aspect of programming, and are an essential tool for automating repetitive tasks. For-loops are typically used when the number of iterations is known before entering the loop, a “While” loop is used to repeat a specific block of code an unknown number of times, until a condition is met and a “Do While” loop is used when we have a conditional execution. Understanding the different types of loops and how to use them effectively is a crucial skill for any programmer.